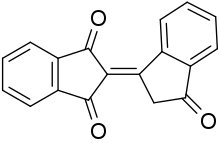
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[1,2′-Biindenylidene]-1′,3,3′(2H)-trione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.415 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 274.275 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 1.444 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 208–211 °C (406–412 °F; 481–484 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bindone is an organic compound with the formula C6H4COCH2C=C(CO)2C6H4. A yellowish solid, it is classified as an aromatic triketone.
Bindone is used as a colour test for the detection of primary amines. It turns violet in their presence. Aromatic amines turn this reagent blue.[2]
Bindone can be prepared by the condensation of two equivalents of 1,3-indandione.[3]
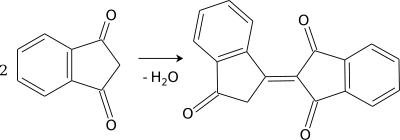
Bindone formation from two molecules of 1,3-indandione
References
- ↑ Wilbuer, Jennifer; Schnakenburg, Gregor; Esser, Birgit (2016). "Syntheses, Structures and Optoelectronic Properties of Spiroconjugated Cyclic Ketones". European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2016 (14): 2404–2412. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201600235.
- ↑ Vecera, Miroslov (2012). Detection and Identification of Organic Compounds. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 319. ISBN 9781468418330.
- ↑ Sharma, Lalit Kumar; Kim, Kyung Bo; Elliott, Gregory I. (2011). "A selective solvent-free self-condensation of carbonyl compounds utilizing microwave irradiation". Green Chemistry. 13 (6): 1546. doi:10.1039/c1gc15164a.
External links
 Media related to Bindone at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bindone at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.