 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Duranest |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a603026 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Parenteral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.296 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
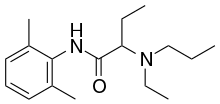
| Formula | C17H28N2O |
| Molar mass | 276.424 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Etidocaine, marketed under the trade name Duranest, is an amide-type local anesthetic given by injection during surgical procedures and labor and delivery. Etidocaine has a long duration of activity, and the main disadvantage of using during dentistry is increased bleeding during surgery.[1]
Synthesis
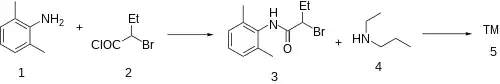
The amide reaction between 2,6-xylidine (1) and 2-bromobutyryl chloride [22118-12-3] (2) gives 2-Bromo-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)Butanamide [53984-81-9] (3). Alkylation with N-Ethylpropylamine [20193-20-8] (4) gives Etidocaine (5).
References
- ↑ Sisk AL (1992). "Long-acting local anesthetics in dentistry". Anesthesia Progress. 39 (3): 53–60. PMC 2148750. PMID 1308373.
- ↑ DE2162744 idem H Adams, G Kronberg, B Takman, U.S. Patent 3,812,147 (1974 to Astra Pharma Prod).
- ↑ Org. Synth. 1950, 30, 62. DOI: 10.15227/orgsyn.030.0062
External links
- Duranest (RxList)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.